Förslag till masterexamensarbeten
Här annonserar vi kontinuerligt nya förslag till examensarbeten på avancerad nivå (GEOR02, 45 hp). De senaste förslagen ligger överst och gamla tas bort efter hand som de blir inaktuella. Kontakta huvudhandledaren om du är intresserad. Du är dessutom alltid välkommen att utifrån dina egna intressen diskutera olika möjligheter med dina lärare. Här kan du se exempel på tidigare masterarbeten. Notera att du måste vara antagen till masterprogrammet i geologi vid Lunds universitet för att kunna genomföra ett av de föreslagna projekten.
Restoring the River Syndan, central Sweden – fluvial processes and river appearance prior to anthropogenic modification
Supervisors: Helena Alexanderson (LU) and Gisela Åberg (Malung-Sälen municipality)
Announced: 2024-09-27
The River Syndan in the mountainous area of central Sweden (Dalarna province) has been strongly altered by humans, for example by straightening the stream channels to improve conditions for log driving. Now the plan is to restore the river to something closer to its former state. To do this, detailed knowledge of the hydromorphology and geological processes in the area is needed to understand what the river looked like and which processes dominated prior to human intervention. By taking on this project, you would contribute that knowledge to the municipality that is leading the restoration work.
The thesis work would include geomorphological and geological mapping of the water course and its surroundings, with focus on fluvial features such as meanders, inactive stream channels and deltas, to provide an overview of the fluvial setting and an interpretation of its long-term evolution. Most of the mapping would be done by remote sensing (digital elevation models, existing maps) but complemented by fieldwork for ground-truthing and for more detailed studies of selected areas. The work will be done in collaboration with the Land- and Water Strategist and the Restoration Project Manager at the Malung-Sälen municipality.
MSc thesis projects with the Lund Luminescence Laboratory
Announced: 2024-01-30
Are you interested in chronology? Are you interested in understanding the progression of climate change, in the evolution of civilisations or in reconstructing past extreme storms? Do you love a combination of field work and lab work? At the Lund Luminescence Laboratory, we use a methodology called luminescence dating to address such research questions in diverse, challenging and exciting places such as Svalbard, Egypt, the Carpathian basin, Cyprus and many places in Scandinavia. We have several ongoing research projects to which master students can contribute:
- What does the light (luminescence) from quartz tell us about sediment transport paths and processes?
- What environmental changes took place in SE Europe during the last glacial-interglacial cycle?
- Does human activity change the properties of quartz?
- When did storms and storm surges hit southern Sweden in the past?
- How has the Scanian coast developed through time?
- How has the relative sea level changed on N Svalbard during the Weichselian glacial period?
- Can Egyptian faience be dated?
- Does micro CT imaging destroy ancient objects?
- How old is the oldest writing system in the world?
If any of this sounds interesting, please contact Helena Alexanderson, Amber Hood or Zoran Perić for more information or discussions of potential thesis topics. More information on some of the projects is presented below.
Reconstruction of climatic and environmental changes during the last glacial-interglacial cycle in the Carpathian Basin
Supervisors: Zoran Perić and Helena Alexanderson
Announced: 2024-01-30
Are you interested in revealing the response of terrestrial systems to past climate changes and the behavior of our atmosphere during the last glacial period? Then this project may be for you.
General information
Loess-palaeosol sequences (LPS) and loess-like sediments are considered as some of the most significant terrestrial archives of climatic change and past atmospheric mineral dust activity, not least due to their nearly continuous deposition. Mineral dust plays an important role in the climate system by interacting with radiation, clouds, and biogeochemical cycles. Loess has great importance in reconstruction of the climate in the past and the loess formations of Central Europe display a close relationship with cooling and warming trends of the Northern Hemisphere during the Pleistocene, thereby sensitively recording regional palaeoclimatic and palaeoecological changes. In general, loess is typical of cold and dry, periglacial climate and environment while the intercalated palaeosols are indicators of warmer and more humid climate, representing interstadials or interglacials.
Main project objectives and methods
The master thesis will focus on the reconstruction of climatic changes and determination of the atmospheric dust activity during the last 30 000 years in Europe. In this project you will use luminescence dating to construct absolute chronologies for one site coupled with magnetic susceptibility measurements of the sediments. This will allow us to determine the timing of sediment deposition, calculate the sedimentation rates and identify potential soil development. The results will yield very reliable indicators on the behavior of the atmosphere and the timing of the main cold and warm periods. The study will also provide completely new insights into the palaeoclimatic changes during the late Quaternary as it will be conducted on thus far uninvestigated sites.
The project will require a sampling field trip to Serbia where the most preserved and complete loess sequences are located. After the sample collection, the focus will be on developing your laboratory skills and gaining basic understanding and expertise in the method of luminescence dating.
Where?
Two uninvestigated sites are available: Vrtište LPS, near the city of Niš in southern Serbia (43° 22′ 13″ S and 21° 48′ 10″ E) and Samoš LPS in the Vojvodina region in northern Serbia (45°12′08″N and 20°46′12″E).
Production and storage of fire derived black carbon in boreal forest soils
Black carbon (BC) is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels and consists of carbon rich aromatic residues (char) and condensed carbon particles (soot). It is found in the atmosphere, ocean and inland waters, soils and sediments. It is of great significance for the carbon cycling on Earth and is one of the most important green-house substances. The high surface area can also function as an absorbent of other organic pollutants. BC particles are resistant to degradation and have a long residence time in soils and sediments and are considered a potential carbon sink. The natural production and storage and of BC in soils are therefore key factors in understanding the carbon cycle.
In this project we will measure BC content in soils from forests that burnt in the summer 2018. Our study sites include 50 forest fire sites from southern to norther Sweden, with additional control plots that have not burnt recently. In a previous study (Eckdahl et al in prep) we show that the BC stocks in the mineral soils doubled as a consequence of the forest fires. In this study we will analyse how and where these additional BC is stored in the mineral soils. The BC in soils can be either bound to mineral grains or as free particles in the soils. The research question is to answer if the added BC is in free particulate form or bound to mineral grains in the soils. This is a key question for understanding the cycling of naturally produced BC.
Project plan
The task is to set up a method for separating the mineral bound BC fraction from the free BC fraction. The separation of the two fractions will be achieved by sieving and heavy-liquid separation. BC of the fractions will be isolated by thermal and chemical oxidation, and quantified by flash-combustion elemental analysis. We will also use spectroscopic methods and microscopy to characterise the BC-fractions, potentially including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and x-ray photon spectroscopy (XPS).
The laboratory work will be at the Department of Geology during spring 2022.
The project can be either set up as a 30 or 45 credit project.
Is this for you?
This project is laboratory intense and is suitable if you want to develop laboratory skills and work in a research project. We think that you have some basic laboratory training from previous courses and want to work with new methods and method development.
Main supervisor: Karl Ljung (Geology Lund Univeristy).
Co-supervisors: Johan Eckdahl (Lund and Umeå Univeristy); Dan Metcalfe (Umeå University); Jeppe Kristensen (Oxford University)
Contact: Karl Ljung, karl [dot] ljung [at] geol [dot] lu [dot] se (karl[dot]ljung[at]geol[dot]lu[dot]se), 046-2223996
Inlagt: 2022-01-03
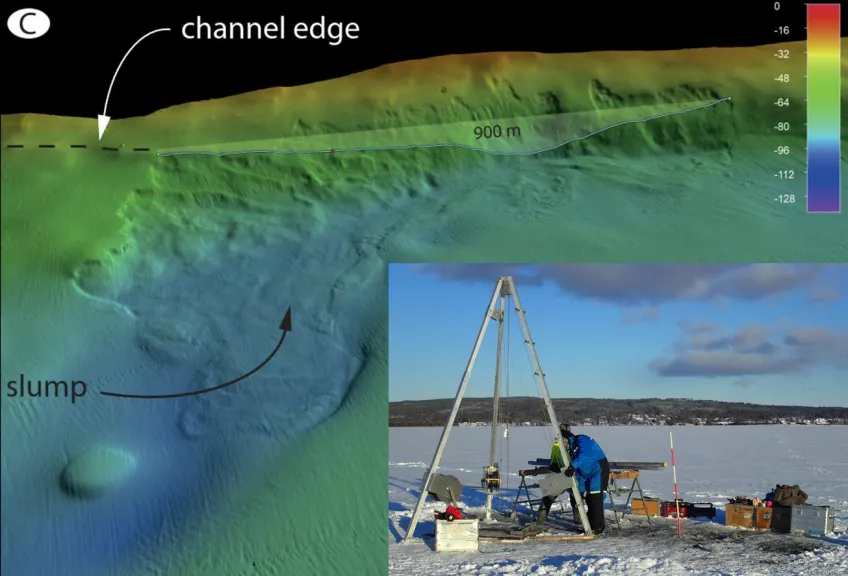
Age and origin of postglacial sediment slumps in Lake Siljan, central Sweden
As part of an ongoing project focussing on the deglaciation dynamics and subsequent lake development of the Siljan region in the county of Dalarna, sediment records from 20-50 m depth in Lake Orsajön have already been obtained. Together with detailed sonar-based bathymetry surveys, these investigations provide evidence of km-sized sediment slumps at great depths that probably took place in the early Holocene. To clarify their timing and triggering processes, similar slump deposits in the even larger and deeper Lake Siljan will be sampled by piston coring in the early spring of 2022. An opportunity for a master thesis project, preferably involving participation in the fieldwork, is offered based on this material. The methods involved will include age determination and age modelling based on radiocarbon dating, lithological and geochemical analyses of lake sediments, as well as interpretation of geophysical data. NOTE: The fieldwork is planned take place during the first week of March, so please let us know as soon as possible if you are interested.
Handledare: Dan Hammarlund, Per Möller, Karl Ljung
Inlagt: 2020-12-02
Solar storms in a paleoperspective
The recent discovery of abrupt short-term radionuclide production rate increases received considerable attention since they can be related to enormous solar storms (see e.g. https://www.iflscience.com/space/traces-giant-solar-storms-found/ ). Such an event could have devastating effects on our technological infrastructure today. Significant efforts are nowadays focusing on high-resolution (annual) 14C measurements in tree rings to identify more of such events. However, ice core 10Be and 36Cl records have the potential to (i) increase the possibility for more reliable detection of such strong solar storm events and (ii) characterise such events in terms of number of particles and energy.
The master thesis will focus on the investigation of potential new solar storm events. It will likely involve ice core sampling at the ice core storage in Copenhagen and it will involve 10Be and 36Cl sample preparation at Lund University. The analysis will include an assessment of the likelihood of the identification of new solar storm event and an assessment of its characteristics.
Handledare: Raimund Muscheler, Florian Mekhaldi
Inlagt: 2019-01-24
Är du geologistudent och intresserad av arkeologi och palynologi?
Skriv ditt examensarbete inom projektet ”Arkeologi i Vännebo – en forskningsundersökning”
VAR?
I Roasjö socken, Svenljunga kommun, Västergötland (ca 20 mil norr om Lund) ligger Vännebosjön. Invid dess östra strand har vid tre tillfällen påträffats ett antal metallföremål som delvis utgjordes av förgyllda ryttardetaljer, vapen med mera som typologiskt kunnat dateras till folkvandringstiden, alltså ca 400-550 e. Kr.
VARFÖR?
Området är förhållandevis okänt trots sitt spektakulära fyndmaterial. Därför vill vi med hjälp av modern arkeologisk metodik och tvärvetenskapliga arbetssätt försöka förstå platsens utveckling under förhistorisk tid i allmänhet och folkvandringstid i synnerhet. Fanns det en boplats i anslutning till offerplatsen, var låg den i så fall? När etablerades den eventuella bebyggelsen och hur har landskapet och vegetationen förändrats i sjöns närhet under mellersta och yngre järnålder?
HUR?
Pollenanalys av sjösedimenten i Vännebosjön, gärna två borrkärnor – det blir Din uppgift!
Övriga tvärvetenskapliga metoder som kommer användas: markkemiska analyser, georadar- och magnetometerundersökningar, metalldetektering.
NÄR?
Målet är att genomföra fältarbetsmomenten (bland annat pollenanalyserna) under 2021 och 2022. Tidsramen är flexibel och beroende på hur analysresultaten faller ut kommer projektet förlängas.
Handledare: Karl Ljung, Anne Birgitte Nielsen
I samarbete med: Elinor Malmberg, Simon Karlsson, Kulturmiljö, VGR
Inlagt: 2021-04-16